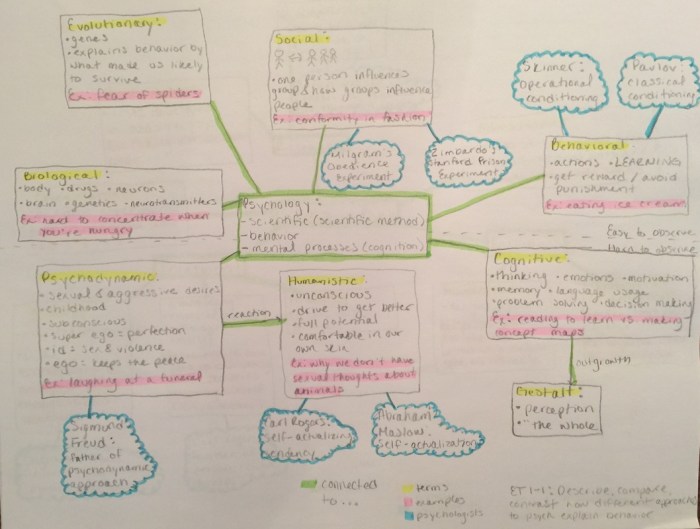
Unit 8 AP Psychology Vocab: A Comprehensive Guide to the Key Terms and Concepts
In this unit, we will explore the fundamental vocabulary of AP Psychology, providing a solid foundation for understanding the complex and fascinating world of human behavior. From cognitive processes to social psychology, we will delve into the key terms that unlock the mysteries of the human mind and its interactions with the world around us.
Vocabulary Terms

In this section, we will delve into the essential vocabulary terms associated with Unit 8 of AP Psychology. These terms are crucial for comprehending the concepts and theories covered in this unit.
Below is a comprehensive list of terms with their definitions:
Personality Theories
- Trait theory: Asserts that personality consists of stable and enduring characteristics that influence behavior across situations.
- Psychodynamic theory: Emphasizes the influence of unconscious conflicts and childhood experiences on personality development.
- Humanistic theory: Focuses on the individual’s potential for growth, self-actualization, and free will.
- Social cognitive theory: Examines how cognitive processes, social learning, and self-efficacy shape personality.
Personality Assessment
- Projective tests: Indirect measures of personality that involve ambiguous stimuli, such as the Rorschach inkblot test.
- Objective tests: Standardized questionnaires that assess personality traits, such as the Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory (MMPI).
- Self-report inventories: Questionnaires in which individuals provide information about their own thoughts, feelings, and behaviors.
- Behavioral observation: Observing and recording an individual’s behavior in different situations.
Personality Disorders
- Antisocial personality disorder: Characterized by a lack of empathy, remorse, and regard for social norms.
- Borderline personality disorder: Involves unstable relationships, intense emotions, and impulsive behaviors.
- Narcissistic personality disorder: Exaggerated sense of self-importance, entitlement, and a need for admiration.
- Obsessive-compulsive personality disorder: Excessive preoccupation with orderliness, perfectionism, and control.
Cognitive Processes
Cognitive processes are mental activities that involve acquiring, storing, retrieving, and transforming information. They include perception, attention, memory, language, problem-solving, and decision-making. In Unit 8 of AP Psychology, we will explore these processes in detail.
Memory
Memory refers to the ability to encode, store, and retrieve information. There are three main types of memory: sensory memory, short-term memory, and long-term memory. Sensory memory stores information for a very brief period, while short-term memory can hold a limited amount of information for a few seconds.
Long-term memory stores information indefinitely and has a much larger capacity.
Attention
Attention is the process of focusing on specific stimuli while ignoring others. It involves selective attention, which allows us to focus on a particular stimulus, and divided attention, which allows us to attend to multiple stimuli at once. Attention is essential for learning and memory, as it helps us to encode and retrieve information effectively.
Language
Language is a system of symbols used to communicate ideas and information. It involves phonology, which is the study of speech sounds, morphology, which is the study of word structure, syntax, which is the study of sentence structure, and semantics, which is the study of word meaning.
Unit 8 AP Psychology vocab has a lot of key terms to remember, but don’t worry, it’s not as daunting as it might seem. If you need a quick break, you can check out the unit 32 pop quiz spanish 2 to practice your language skills.
Once you’re refreshed, come back and tackle those psychology terms like a pro!
Language is essential for social interaction and for expressing our thoughts and feelings.
Biological Bases of Behavior
Our thoughts, feelings, and actions are all influenced by the intricate workings of our biological systems. In this section, we will explore the biological foundations of behavior, examining how the brain and nervous system shape our cognitive processes and overall conduct.
The Nervous System, Unit 8 ap psychology vocab
The nervous system, a complex network of cells and tissues, serves as the primary communication system within our bodies. It can be divided into two main components:
- Central Nervous System (CNS):Consists of the brain and spinal cord, which process and transmit information.
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS):Comprises all nerves outside the CNS, carrying messages to and from the CNS.
Social Psychology
Social psychology explores the influence of social factors on individuals’ thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. It examines how our interactions with others shape our perceptions, attitudes, and actions.
Key concepts in social psychology include:
Social Influence
- Conformity:Adjusting one’s behavior to match the group’s norms.
- Compliance:Changing behavior in response to direct requests or orders.
- Obedience:Following orders from an authority figure, even if they conflict with personal beliefs.
Attitudes and Prejudice
- Attitudes:Learned predispositions to respond favorably or unfavorably to certain objects, people, or ideas.
- Prejudice:Unfavorable attitudes toward an entire group of people based on stereotypes.
- Discrimination:Unfair treatment based on prejudice.
Social Cognition
- Attribution:Explaining the causes of behavior, either internally (personal factors) or externally (situational factors).
- Heuristics:Mental shortcuts used to simplify decision-making.
- Cognitive dissonance:Uncomfortable tension experienced when holding two conflicting beliefs.
Developmental Psychology: Unit 8 Ap Psychology Vocab

Developmental psychology examines how individuals change and develop throughout their lifespan. Cognitive development refers to changes in intellectual abilities, including perception, attention, memory, language, and problem-solving. Social development encompasses changes in social behavior, relationships, and interactions with others.
Cognitive Development
Piaget’s stages of cognitive development
Sensorimotor, Preoperational, Concrete Operational, Formal Operational
Vygotsky’s sociocultural theory
Emphasizes the role of social interactions and culture in cognitive development
Information processing theory
Views cognitive development as a gradual improvement in processing speed and capacity
Social Development
Attachment theory
Examines the development of emotional bonds between children and their caregivers
Erikson’s stages of psychosocial development
Artikels challenges and tasks faced at different stages of life
Kohlberg’s stages of moral development
Describes the development of moral reasoning and ethical decision-making
Applications
The concepts covered in Unit 8 of AP Psychology have wide-ranging applications in the real world. By understanding these concepts, we can gain insights into human behavior and develop strategies to improve it.
One of the most important applications of AP Psychology is in the field of education. By understanding how people learn and remember, educators can create more effective teaching methods. For example, the concept of cognitive dissonance suggests that people are motivated to reduce inconsistency between their beliefs and behaviors.
This principle can be used to design educational experiences that challenge students’ beliefs and encourage them to think critically.
Applications in Healthcare
AP Psychology concepts are also used in the field of healthcare. For example, the concept of stress can be used to understand how stress affects physical and mental health. This knowledge can be used to develop stress-management programs that can help people cope with stress and improve their overall well-being.
Applications in Business and Industry
AP Psychology concepts are also used in business and industry. For example, the concept of motivation can be used to understand what motivates employees and how to create a more motivating work environment. This knowledge can be used to improve employee productivity and satisfaction.
FAQ Corner
What is the significance of vocabulary in AP Psychology?
Vocabulary forms the foundation of AP Psychology, providing the precise language necessary to describe and analyze psychological phenomena.
How can I effectively memorize the vocabulary terms?
Use flashcards, practice active recall, and engage in discussions to enhance your retention of vocabulary terms.
What are some tips for applying vocabulary terms in essays?
Use vocabulary terms accurately and precisely, providing specific examples to demonstrate your understanding.