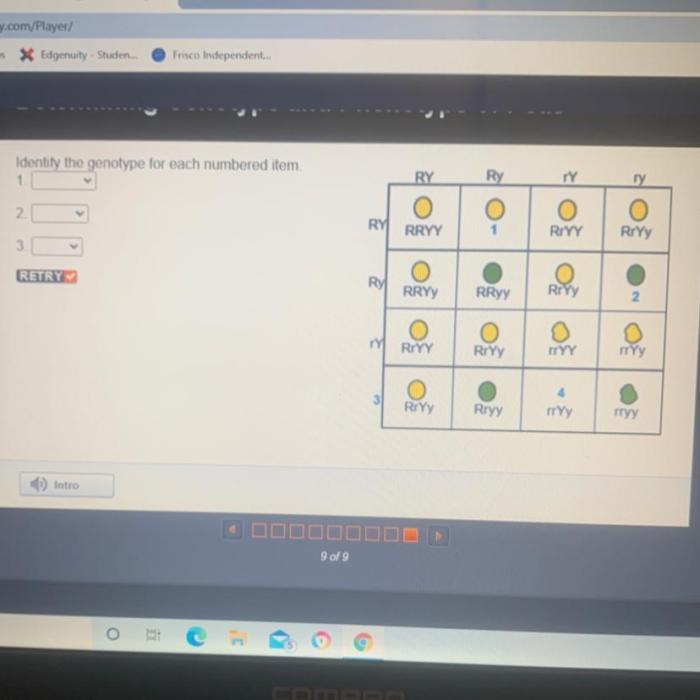
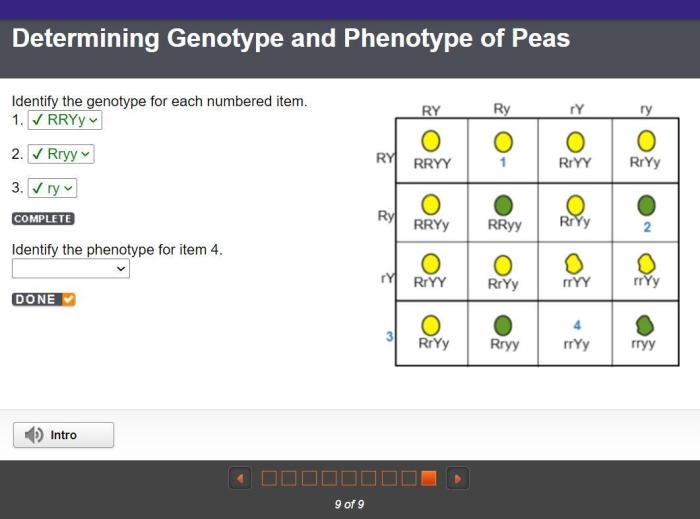
Identify the genotype for each numbered item. 1. 2. 3. – Beginning with the identification of genotypes for each numbered item (1, 2, and 3), this discourse ventures into the captivating realm of genetics, where we unravel the significance of genotype analysis and its diverse applications across multiple disciplines.
This exploration delves into the fundamental concept of genotype, examining its role in genetic studies and the methodologies employed to determine genotypes, including DNA sequencing and genotyping arrays.
Genotype Identification
Genotype identification is the process of determining the genetic makeup of an individual organism. It involves identifying the alleles present at specific genetic loci, which are the specific locations on chromosomes where genes are located. Genotype identification is crucial in various fields, including medicine, agriculture, and forensics.
Methods of Genotype Identification
- DNA sequencing:This method involves determining the order of nucleotides in a DNA sample, which provides information about the alleles present at specific loci.
- Genotyping arrays:These are high-throughput platforms that allow for the simultaneous analysis of multiple genetic loci, providing a cost-effective and efficient method for genotype identification.
Genotype Analysis
Concept of Genotype
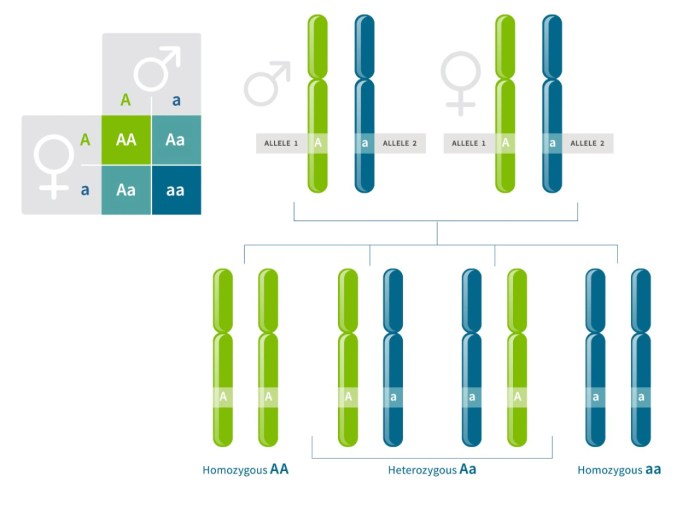
A genotype refers to the specific combination of alleles present at a particular genetic locus. Alleles are different versions of a gene that occupy the same locus on homologous chromosomes. The genotype of an individual can be homozygous (two identical alleles) or heterozygous (two different alleles).
Significance of Genotype Analysis, Identify the genotype for each numbered item. 1. 2. 3.
Genotype analysis plays a vital role in genetic studies as it provides insights into the genetic basis of traits, diseases, and other biological processes. By identifying genotypes, researchers can:
- Predict disease risk:Certain genotypes have been associated with an increased or decreased risk of developing specific diseases.
- Improve crop yields:Genotype analysis can help identify plants with desirable traits, such as resistance to pests or increased yield, for selective breeding.
- Solve crimes:Genotype identification is used in forensic science to identify individuals through DNA profiling and to establish paternity or kinship.
Ethical Considerations
Genotype identification raises important ethical concerns related to privacy, genetic discrimination, and the potential misuse of genetic information. It is essential to:
- Obtain informed consent:Individuals should be fully informed about the implications of genetic testing and provide their consent before undergoing such procedures.
- Protect privacy:Genetic information is highly sensitive and should be protected from unauthorized access and misuse.
- Prevent genetic discrimination:Laws and regulations should be in place to prohibit discrimination based on genetic information in areas such as employment and insurance.
FAQs: Identify The Genotype For Each Numbered Item. 1. 2. 3.
What is the significance of genotype identification?
Genotype identification provides valuable insights into an individual’s genetic makeup, enabling the prediction of disease risk, optimization of crop yields, and resolution of criminal cases.
How are genotypes typically identified?
Genotypes are commonly identified through DNA sequencing or genotyping arrays, which analyze the DNA sequence to determine the specific genetic variants present.
What are the ethical considerations associated with genotype identification?
Ethical considerations include obtaining informed consent, protecting privacy, and preventing genetic discrimination, ensuring the responsible use of genotype information.