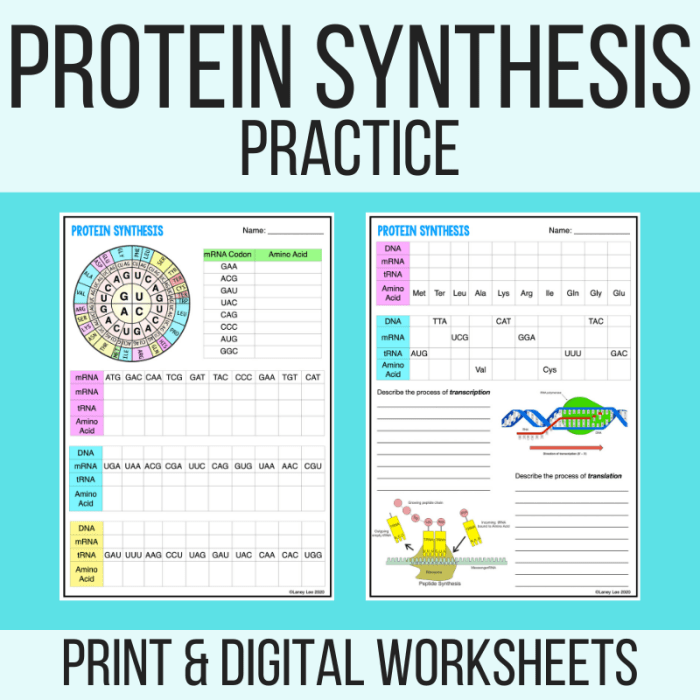
Dive into the intricate world of protein synthesis with our comprehensive protein synthesis practice worksheet answers. This guide unveils the secrets of this fundamental biological process, empowering you with a deep understanding of its mechanisms and significance.
Our meticulously crafted answers provide clarity and insight into every aspect of protein synthesis, from the central dogma to the regulation of protein expression. Prepare to unravel the complexities of molecular biology and gain a newfound appreciation for the wonders of life.
Protein Synthesis Overview
Protein synthesis is the process by which cells create proteins, which are essential for a wide range of biological functions. The central dogma of molecular biology describes the flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA to protein.
DNA contains the genetic code that specifies the sequence of amino acids in a protein. During transcription, DNA is used as a template to create messenger RNA (mRNA), which carries the genetic information to the ribosome. At the ribosome, mRNA is translated into a chain of amino acids, which are linked together to form a protein.
The process of protein synthesis is essential for the growth and development of organisms. It also plays a role in cell repair, metabolism, and immune function.
Transcription Process
Initiation, Protein synthesis practice worksheet answers
Transcription begins with the binding of RNA polymerase to a specific DNA sequence called the promoter. RNA polymerase then unwinds the DNA and begins to synthesize mRNA.
Elongation
During elongation, RNA polymerase continues to add nucleotides to the growing mRNA molecule. The sequence of nucleotides in mRNA is determined by the sequence of nucleotides in DNA.
Termination
Transcription ends when RNA polymerase reaches a specific DNA sequence called the terminator. RNA polymerase then releases the mRNA molecule and dissociates from the DNA.
Translation Process
Initiation, Protein synthesis practice worksheet answers
Translation begins with the binding of a ribosome to mRNA. The ribosome then scans the mRNA until it finds the start codon (AUG).
Elongation
During elongation, the ribosome moves along the mRNA, adding amino acids to the growing polypeptide chain. The sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide chain is determined by the sequence of codons in mRNA.
Termination
Translation ends when the ribosome reaches a stop codon (UAA, UAG, or UGA). The ribosome then releases the polypeptide chain and dissociates from the mRNA.
Protein Structure and Function

Primary Structure
The primary structure of a protein is the sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide chain.
Secondary Structure
The secondary structure of a protein is the way in which the polypeptide chain folds into a regular pattern. The most common secondary structures are the alpha helix and the beta sheet.
Tertiary Structure
The tertiary structure of a protein is the three-dimensional shape of the protein. The tertiary structure is determined by the interactions between the amino acids in the polypeptide chain.
Quaternary Structure
The quaternary structure of a protein is the way in which multiple polypeptide chains come together to form a single protein complex.
Regulation of Protein Synthesis
Transcriptional Control
Transcriptional control is the regulation of gene expression at the level of transcription. Transcriptional control can be achieved by a variety of mechanisms, including the binding of transcription factors to DNA.
Translational Control
Translational control is the regulation of gene expression at the level of translation. Translational control can be achieved by a variety of mechanisms, including the binding of regulatory proteins to mRNA.
FAQ: Protein Synthesis Practice Worksheet Answers
What is the central dogma of molecular biology?
The central dogma describes the flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA to proteins, providing a blueprint for cellular function.
What is the role of ribosomes in protein synthesis?
Ribosomes serve as the protein synthesis machinery, reading the mRNA sequence and assembling amino acids into a polypeptide chain.
How is protein synthesis regulated?
Protein synthesis is tightly regulated through transcriptional and translational control mechanisms, ensuring the production of the right proteins at the right time.